Which Of The Following Carbohydrates Is Used To Store Energy In Animal Cells
3. Carbohydrates, Structures and Types
This chapter provides an introduction and word of carbohydrates that are important in the nutrition of nutrient-producing animals.
New Terms
Amylopectin
Amylose
Cellulose
Disaccharide
Fructose
Galactose
Glucose
Glycogen
Heteropolysaccharide
Homopolysaccharide
Monosaccharide
Oligosaccharide
Polysaccharide
Starch
Trisaccharide
Chapter Objectives
- To nowadays the chemical construction of unlike types of carbohydrates and their importance in animal nutrition
Carbohydrates
What Are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are the major components of establish tissue, making up to threescore% to 90% of the dry matter (DM). Carbohydrates incorporate carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in the proportion found in water (CHtwoO) and are hence hydrates of carbon. Carbohydrates are the bones energy source in animal cells. Dietary carbohydrates obtained from plant-based products serve as a major source of energy for the animate being. The chlorophyll in institute cells traps solar energy and produces carbohydrates using carbon dioxide and water and gives off oxygen, as shown in the following equation:
solar energy + half-dozen CO2 + six H20 → C6H2O + 6 O2.
Carbohydrates are the major dietary source of energy for animals.
In the plant cell, carbohydrates could be nowadays in the cell content equally sugar or starch, or they could be associated with the cell wall structure (e.g., cellulose). When animals eat plant materials (e.g., cereal grains, grass, fodder), energy in the feed'south carbohydrates is made available through metabolic processes in the beast prison cell. Overall, animal metabolism produces free energy in a reverse procedure to that of photosynthesis.
Beast metabolism produces energy in a reverse process to that of photosynthesis in plants.
Structure and Classification
One method of classifying carbohydrates is based on the number of carbon atoms per each molecule of a carbohydrate and on the number of molecules of saccharide in the chemical compound. Based on the number of carbon atoms, a carbohydrate can be classified as triose (3 C), tetrose (4 C), pentose (v C), and hexose (vi C). The suffix "ose" at the stop of a biochemical proper name flags the molecule as a "sugar." Among these, pentoses (east.g., ribose in ribonucleic acid (RNA)) and hexoses (e.g., glucose, or claret saccharide) are the most common sugars in fauna tissues. Based on the number of molecules of saccharide in the compound, carbohydrates tin exist classified every bit (ane) monosaccharide, one unit of measurement of sugar; (two) disaccharide, two monosaccharides; (3) oligosaccharide, 3 to fifteen monosaccharides; and (4) polysaccharides, big polymers of simple sugars.
A. Monosaccharides are often referred to every bit uncomplicated sugars (e.thou., glucose) and cannot be hydrolyzed into simpler compounds.
Monosaccharides tin can exist subdivided based on the number of carbon (C) atoms. The following listing shows the prefixes for numbers of carbons in a sugar.
- Triose (3 C)
- Tetrose (iv C)
- Pentose (five C; e.g., Xylose and Ribose)
- Hexose (half dozen C; e.one thousand., glucose, fructose, galactose, and mannose)
Monosaccharides are the simplest forms of carbohydrate.
Most monosaccharides in creature tissues are of 5 C and half dozen C sugars. Simple sugars are too subdivided into aldose, a sugar that contains an aldehyde structure, or ketose, a sugar that contains a ketone group. Both glucose and fructose accept the same molecular formula C6H12O6 and are hexoses (6 C). Just glucose is an aldose (also called aldohexose) and fructose is a ketose, or a ketohexose.
The three hexoses that are nutritionally and metabolically important are glucose, fructose, and galactose (see Figure 3.1).
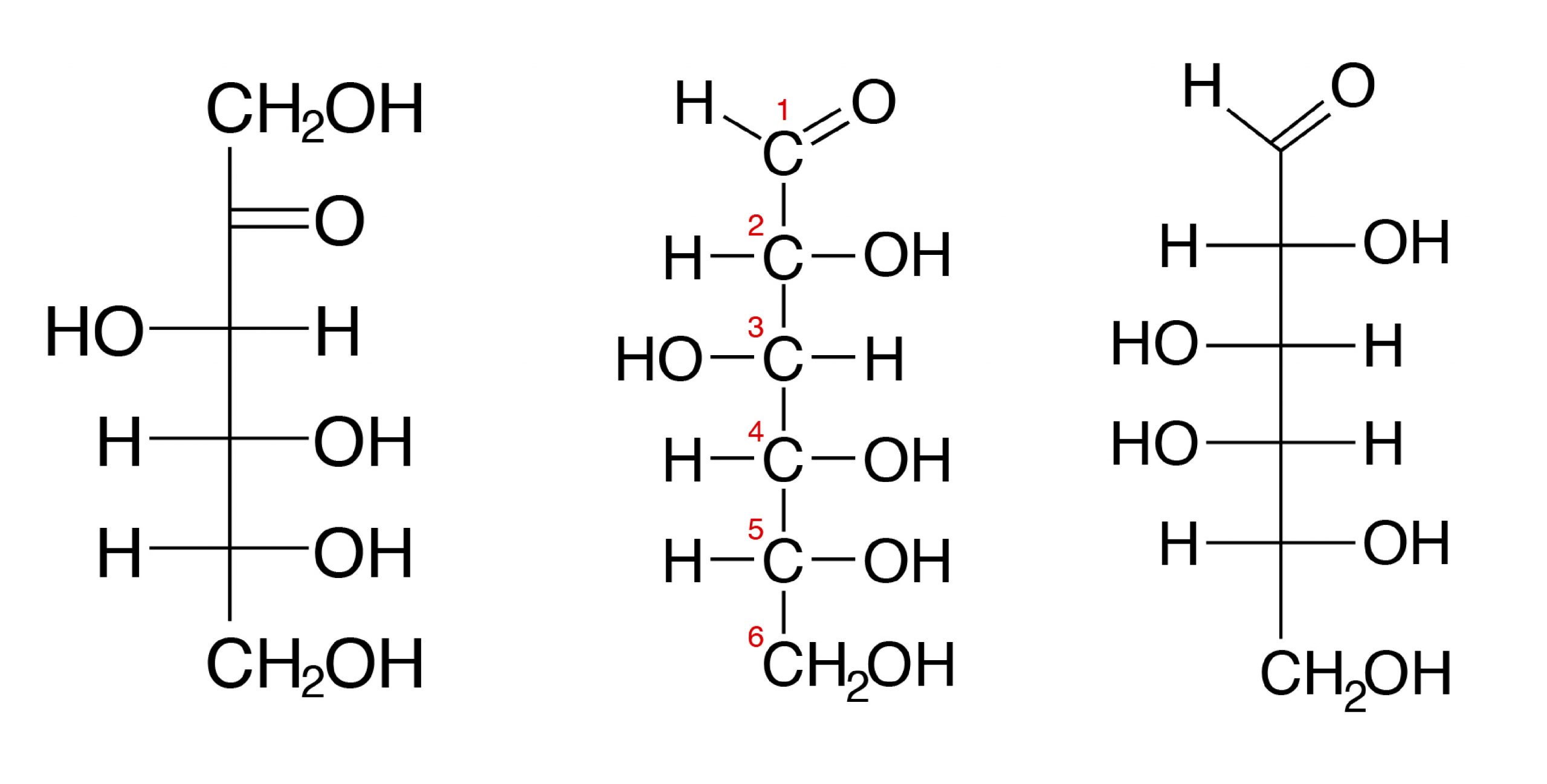
Nigh nutritionally of import sugars are pentoses or hexoses.
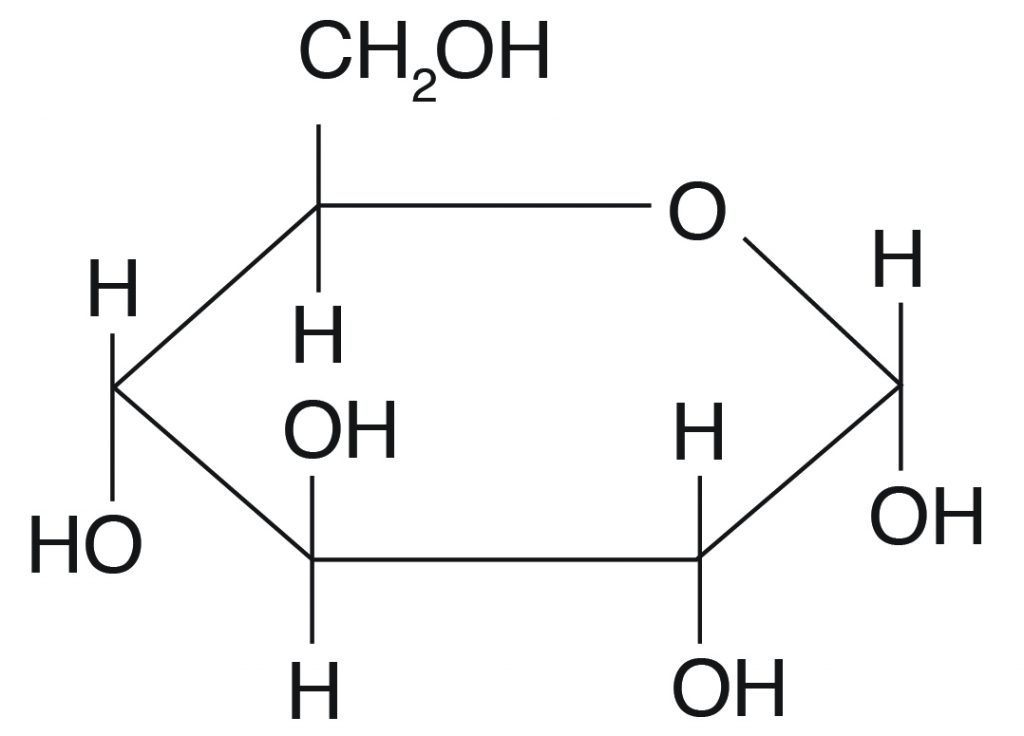
The chemic structure of glucose can be represented as a straight chain form (Figure 3.i) and in circadian course (also shown in Figure three.1). In a biological organisation, glucose exists primarily equally a cyclic form and very rarely in a straight form (in aqueous solution). Glucose is the course of carbohydrates found in circulating claret (blood sugar) and is the primary carbohydrate used by the trunk for free energy production. Fructose, or "fruit sugar," is found in ripened fruits and beloved and is also formed by digestion of disaccharide sucrose. Galactose is institute along with disaccharide lactose in mammalian milk and is released during digestion.
Glucose can be as α and β isomers and has immense animal nutritional implications. These two isomers differ in their orientation of OH on C #1 (shown in red in Effigy 3.ii).
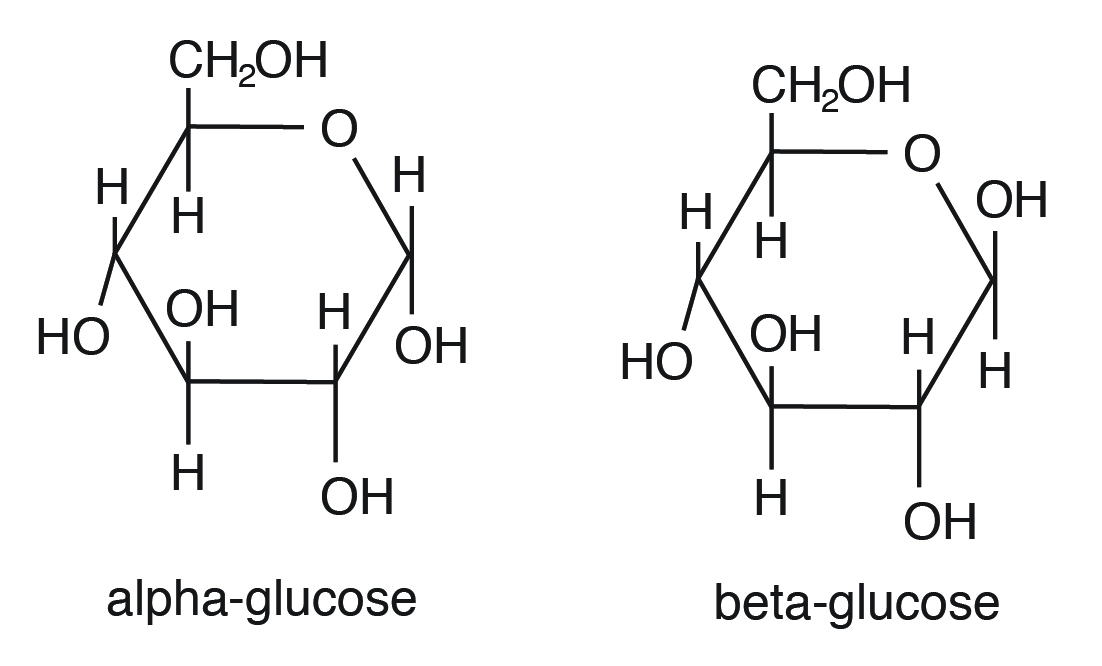
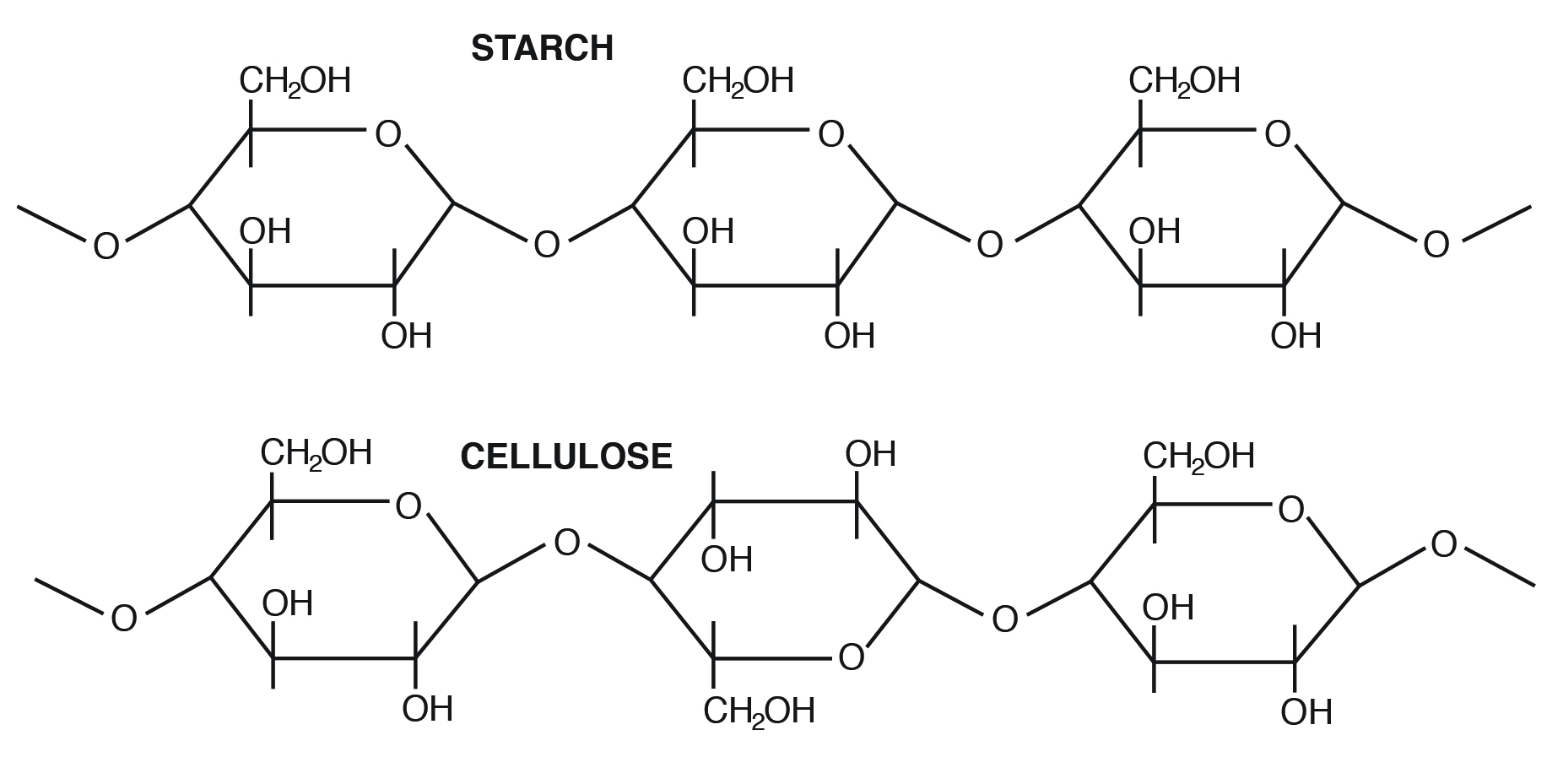
For example, starch contains α-D-Glucose, while cellulose has rigid polymers with β-D-Glucose. Nutritionally important sugars are of the D-form (non the Fifty-form). D and L refer to stereo-orientation at disproportionate carbon position 5 in a hexose or carbon position four in a pentose.
Nutritional of import sugars are of the D-course.
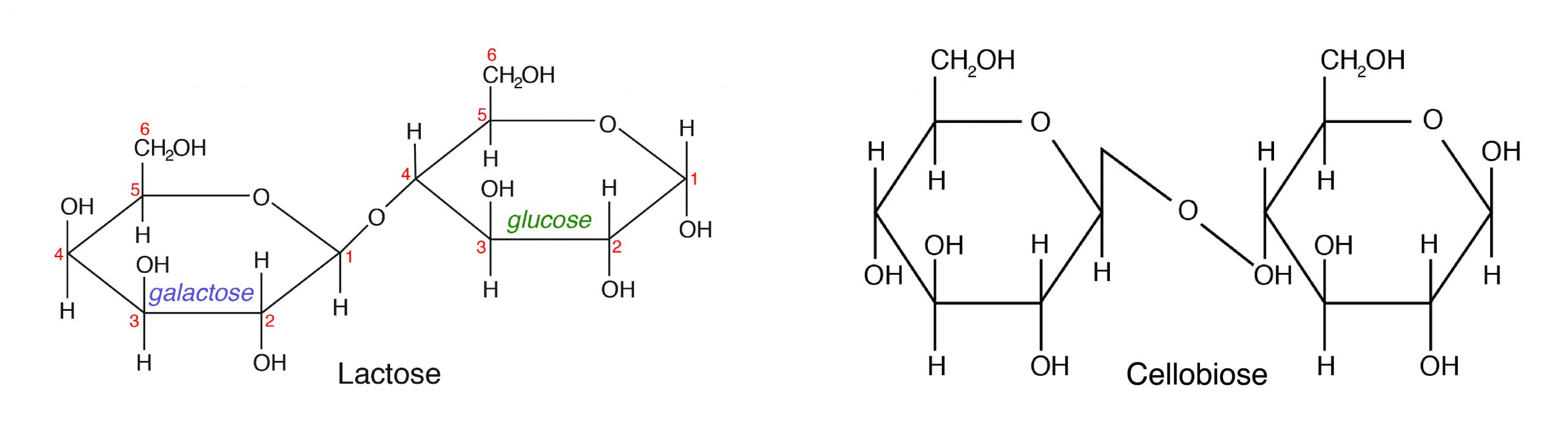
B. Disaccharides are fabricated up of 2 monosaccharides bonded together past a glycosidic (covalent) bond. The post-obit are some of the common disaccharides:
- Sucrose-glucose + fructose (e.g., table sugar)
- Lactose-glucose + galactose (milk saccharide)
- Maltose-α-D-Glucose + β-D-Glucose (malt sugar)
- Cellobiose-β-D-Glucose + β-D-Glucose (cellulose)
Among the different disaccharides, lactose (milk saccharide) is the but sugar of animal origin. Even so, cellobiose every bit a component of cellulose is important in animal nutrition. Monogastric animals cannot digest cellulose because they do not produce the cellulase enzyme that can split β-D-Glucose.
C. Oligosaccharide are fabricated by bonding together three or more than (three to fifteen) monosaccharides bonded together.
- Raffinose (glucose + fructose + galactose; 3 sugars)
- Stachyose (glucose + fructose + two galactose; 4 sugars)
In creature diets, oligosaccharides are normally found in beans and legumes. Some oligosaccharides are used as substances to enhance the growth of adept microbes (prebiotics). Recently, there has been an increased interest in the use of different oligosaccharides equally feed additives to heighten hindgut health (e.g., fructooligosaccharides, mannan oligosaccharides).
D. Polysaccharides, every bit their proper noun implies, are made by joining together large polymers of uncomplicated sugars.
Polysaccharides are the most of import saccharide in creature feed. Polysaccharides are composed of many unmarried monosaccharide units linked together in long, complex bondage. The functions of polysaccharides include free energy storage in constitute cells (eastward.g., seed starch in cereal grains) and animate being cells (due east.g., glycogen) or structural support (found fiber). Components of cell wall structure are also called nonstarch polysaccharides, or resistant starch, in animal diet, as they cannot be digested by animate being enzymes only are fermented by hindgut and rumen microbes.
Polysaccharides can be homopolysaccharides or heteropolysaccharides.
- a. Homopolysaccharide
- b. Heteropolysaccharide
a. Homopolysaccharide: Contains just one type of saccharide unit.
Examples of homopolysaccharides that are important in fauna diet include starch (nonstructural form), glycogen (animal form), and cellulose (establish structural form).
- Starch: Main sugar form of saccharide in cereal grains (seed free energy storage). The bones unit is α-D-Glucose. Forms of starch in cereal grains include
- Amylose-α 1,4 linkage-straight chain, nonbranching, helical construction
- Amylopectin-α ane,4 linkage with alpha i,6 linkage at branch points
Amylose is the simplest of the polysaccharides, beingness comprised solely of glucose units joined in an alpha i,iv linkage (Figure 3.four). Amylose is water soluble and constitutes 15% to 30% of full starch in most plants.
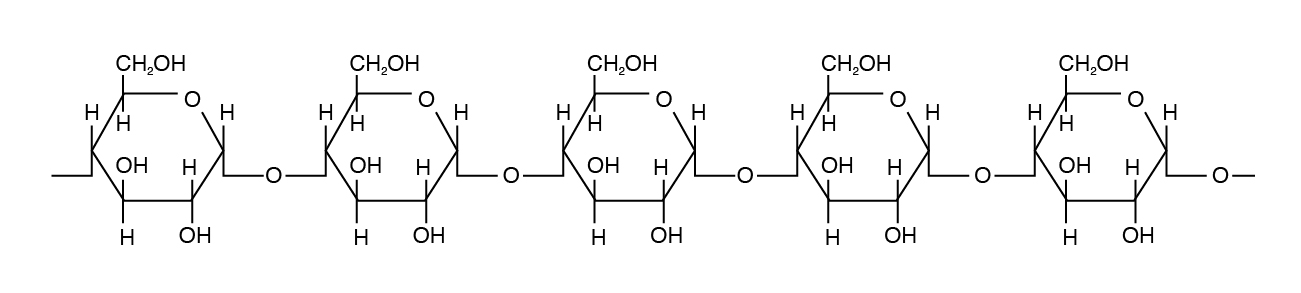
Amylopectin differs in how the glucose units are joined together. Alpha ane,4 linkages predominate, but a "co-operative" arises from an alpha 1,six linkage. Such branches brand the structure of amylopectin more complex than that of amylose. Amylopectin is not water soluble and constitutes 70% to 85% of total starch in plant cells.
Starch is the chief sugar source in the diet of monogastric animals.
Amylopectin is the major class of starch in plant cells.
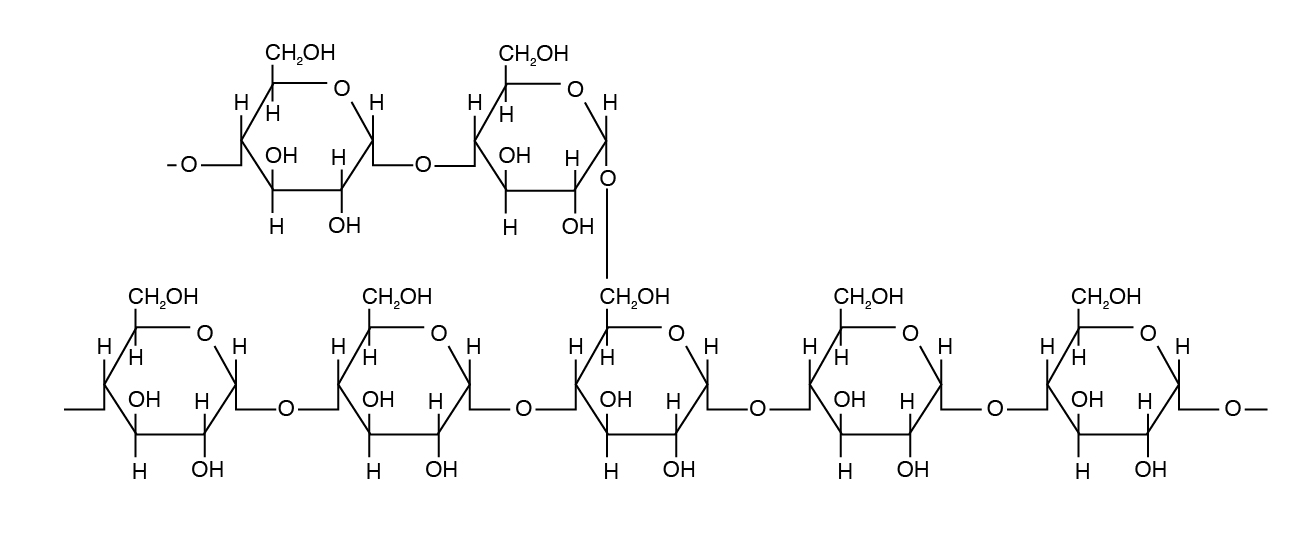
Glycogen is a class of starch found in fauna tissue and is hence chosen animate being starch. Glycogen is a polysaccharide that is physically related to amylopectin with bones alpha-D-Glucose but has a mix of α 1,4 and α one,6 bonds. Glycogen exists in a small corporeality (< 1%) in liver and musculus tissue.
Cellulose is the most abundant carbohydrate in nature. It provides structural integrity to institute cell walls. The basic unit is β 1,iv linkage, straight concatenation, nonbranching (Figure three.three). Cellulose is highly stable. No animal enzyme can pause information technology; only microbial cellulase can degrade it. Ruminant animals such every bit cattle, however, take bacteria in their rumen that contain the enzyme cellulase. It breaks the beta 1,4 links of the glucoses in cellulose to release the sugar for free energy.
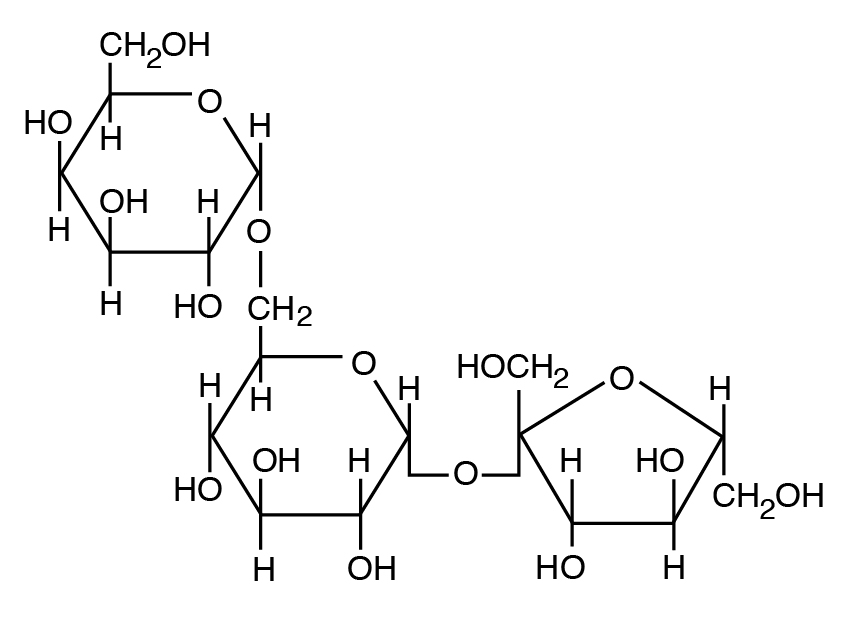
b: Heteropolysaccharide: A component of plant cell walls with a mix of 5 C and 6 C sugars (e.m., hemicellulose and pectin, a mixture of pentose and hexose units).
Key Points
- Carbohydrates are "hydrates of carbon" and have the generic structure of C(n)H(2n)O(n).
- A single sugar unit is a monosaccharide. These can consist of 3-carbon moieties (triose), four-carbon units (tetrose), five-carbon moieties (pentose), and half dozen-carbon moieties (hexose).
- Well-nigh nutritionally important sugars are pentoses or hexoses.
- Further classification of sugars is a definition of either aldose (having an aldehyde group) or ketose (having a ketone group). Glucose, mannose, and galactose are aldoses, whereas fructose is a ketose.
- Nutritionally important sugars are of the D-grade (not the L-form). D and 50 refer to stereo-orientation at asymmetric carbon position five in a hexose or carbon position 4 in a pentose.
- Sugars link together via a glycosidic bond to form di- (two monosaccharides) or oligo- (3 to 15 monosaccharides), and polysaccharides.
- The nature of glycosidic bonds influences the structural and chemic properties of the sugars and influences their ease of digestion. Sugars that bond via an blastoff ane,4 linkage may be digested by mammalian enzymes. Sugars that are linked via the beta one,iv linkage are resistant to digestion.
- Nutritionally significant disaccharides are sucrose and lactose.
- Starch from plants serves as a major energy source in animal diets. Starch consists of ii types of molecules: amylose (alpha i,4 linked glucose) and amylopectin (alpha one,four and alpha 1,six linked glucose).
- Glycogen, a storage grade of carbohydrates in the liver and muscles, is very similar to starch also called beast starch.
- Plant polysaccharides likewise include cellulose and hemicellulose and pectin (nonstarch polysaccharides). Mammalian enzymes cannot degrade these polysaccharides to complimentary sugars, but microbial enzymes tin handle them.
Review Questions
- In what important ways do starch and cellulose differ?
- What are the disaccharides of nutritional significance?
- Nutritional important sugars are of the D-grade or the L-form?
- The most important sugar in diet
- List the 2 forms in which starch exist
- The forms of starch in the animal body is?
- A structural homopolysaccharide made of glucose is
- cellulose
- hemicellulose
- pectin
- raffinose
- Amongst these unlike sugars, the principal source of energy for a broiler chicken is
- fructose
- sucrose
- glycogen
- glucose
- Two molecules of carbohydrate are linked together by this bond
- peptic bond
- glycosidic bond
- diglyceride bond
- both a) and b)
- Amid the 2 forms of starch, this is the major component of cereal grains
- amylose
- amylopectin
- cellulose
- glycogen
Source: https://open.oregonstate.education/animalnutrition/chapter/chapter-3/
Posted by: bivenscovest.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Which Of The Following Carbohydrates Is Used To Store Energy In Animal Cells"
Post a Comment